Understanding Welding Positioner Types
Welding positioners have become indispensable tools in metal fabrication, but choosing between portable and industrial models requires careful consideration. These two categories serve distinct purposes in modern manufacturing environments.
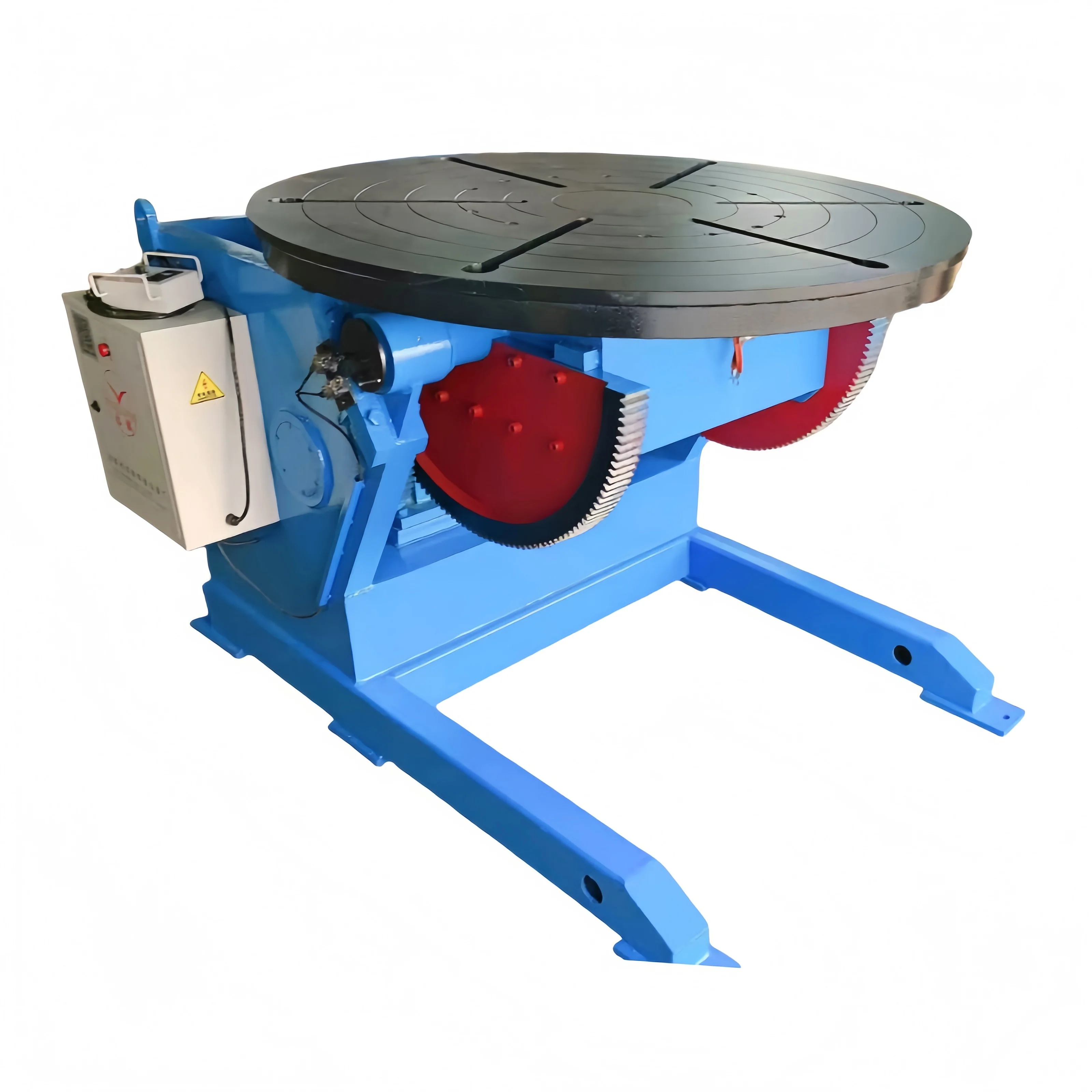

Figure 1: Industrial Welding Positioner
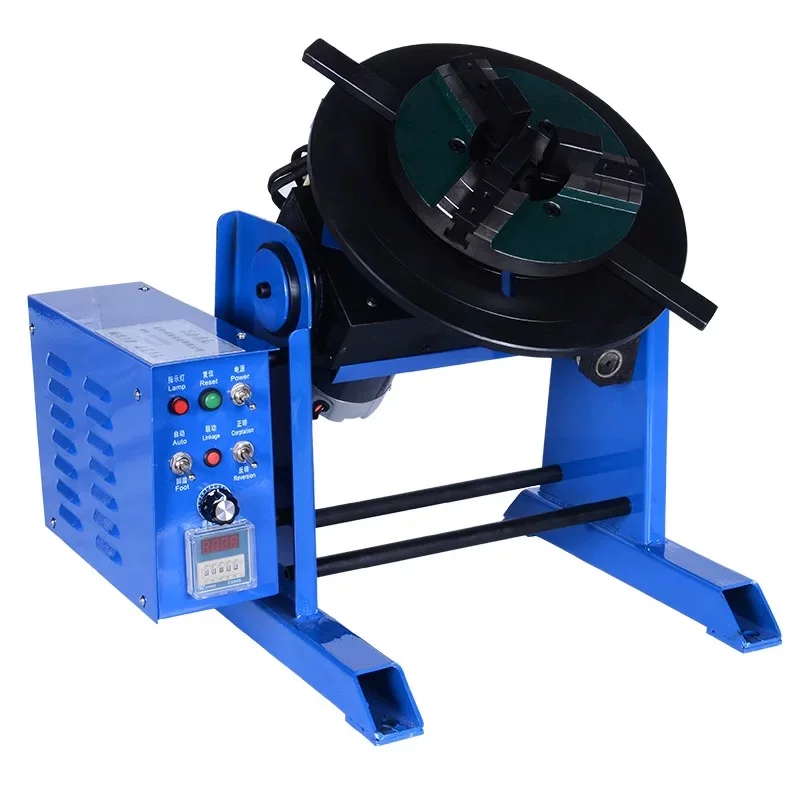

Figure 2: Portable welding Positioner
Mobility and Application Scope
Portable welding positioners excel in scenarios demanding flexibility:
- On-site repair work for immobile equipment
- Small-batch welding of hardware components
- Educational demonstrations in trade schools
- Temporary construction site needs
- Artistic metal fabrication projects
Their compact design allows quick setup and easy transportation between job sites.
Industrial welding positioners form the backbone of production lines:
- Automotive body welding stations
- Circumferential welding in pressure vessel manufacturing
- Heavy structural component welding
- Precision aerospace part fabrication
- Shipbuilding section assembly
Engineered for continuous operation, these units ensure consistent weld quality in high-volume production.
Structural Design and Load Capacity
Portable Unit Characteristics:
- Aircraft-grade aluminum or composite frames
- Foldable or modular configurations
- Typical weight: 20-50kg (44-110lbs)
- Integrated carrying handles or wheel kits
- Maximum capacity: 50-100kg (110-220lbs)
Industrial Unit Features:
- Q345B steel or HT250 cast iron construction
- Monolithic welded or cast bases
- Weight range: 500kg-10 metric tons
- Foundation mounting options
- Capacity options: 1-50 metric tons
- Optional seismic reinforcement
Drive Systems and Motion Control
Portable Positioner Mechanics:
- Manual worm gear adjustments
- DC brushed or stepper motor options
- Speed range: 1-10 RPM
- Basic potentiometer speed control
- Optional wireless remote operation
- Typical accuracy: ±1°
Industrial-Grade Technology:
- AC servo or hydraulic drive systems
- Precision gear reducers
- High-resolution absolute encoders
- Multi-axis interpolation capability
- Speed range: 0.1-30 RPM
- Repeatability: ±0.05°
- Advanced motion control features
Operational Stability and Precision
Portable units show limitations in precision maintenance:
- Structural flex under load
- Mechanical backlash in drive trains
- Thermal drift effects
- Accuracy degradation after 4-6 hours
- Daily variation up to ±1.5°
- Accelerated wear in moving components
Industrial models maintain exceptional stability:
- FEA-optimized rigid structures
- Adjustable preload bearing systems
- Thermal compensation algorithms
- Hardened guideways (HRC50+)
- 24/7 operation with <±0.1° variation
- 1,000,000+ cycle lifespan
- Automatic lubrication systems
Environmental Considerations
Portable Unit Limitations:
- Open-frame cooling design
- Basic splash protection (IP54)
- Limited EMI resistance
- Operating range: 0-40°C
- Not recommended for dusty environments
Industrial-Grade Protection:
- Totally enclosed construction (IP65)
- Double-sealed critical components
- EMI/RFI shielding
- Extended temperature range (-20°C to 55°C)
- Molten metal splash guards
- Corrosion-resistant finishes
- Explosion-proof options
Why Industrial Positioners Remain Essential
1. Heavy-Duty Performance
Massive components like ship sections require robust support structures that portable units simply cannot provide.
2. Precision Demands
Aerospace and nuclear applications demand sub-degree accuracy maintained over years of service.
3. Automation Integration
Modern smart factories require seamless communication between welding robots and positioners.
4. Long-Term Reliability
Industrial units offer decade-long service life with proper maintenance.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Certified safety features meet stringent industry standards.
For manufacturers evaluating positioner options, consider:
- Project scale and duration
- Available workspace
- Budget constraints
- Future expansion plans
While portable welding positioners offer convenience for mobile applications, industrial welding positioners deliver unmatched performance for demanding production environments. Their superior durability, precision, and integration capabilities make them irreplaceable in heavy manufacturing sectors.
For optimal results, consult with welding automation specialists to match equipment capabilities with your specific application requirements. Proper positioner selection significantly impacts weld quality, production efficiency, and overall equipment lifecycle costs.










Comments (0)